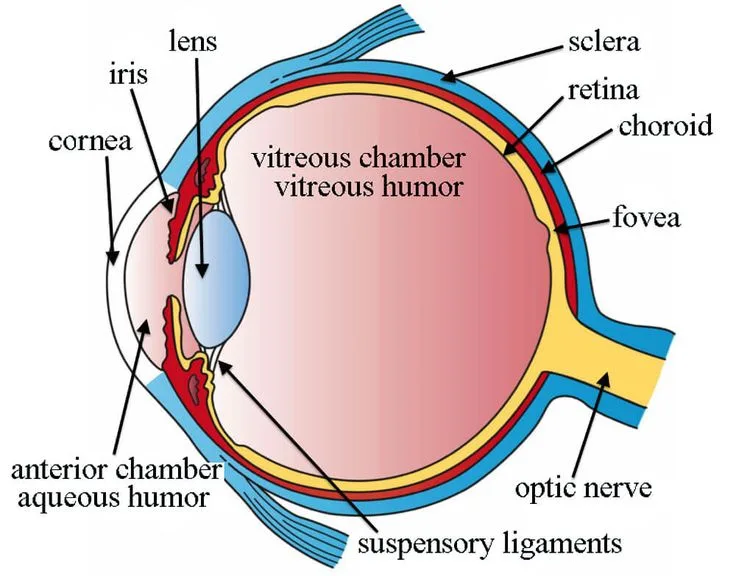
Human eye and colourful world important questions for 2024-25 boards exam.
- Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions:
- Human eye and colourful world important questions: MCQ:
- Human eye and colourful world important questions: Very Short Answer Questions:
- Human eye and colourful world important questions: Short Answer Questions:
- Human eye and colourful world important questions: Long Answer Questions:
Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions:
We are providing you the Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions for 2024-25 preparation of your board exam.
Theses are the Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions. These Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions will help you to preapare better for your exam. So try these Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions.
These Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions are provided in this website and the Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions PDF download link is given at the extreme bottom.
Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions. These are the Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions, you can practise them from here. For later use, download the pdf from the Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions PDF download link given below.
Human eye and colourful world important questions: MCQ:
Q) At noon the sun appears white as
(a) light is least scattered.
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away.
(c) blue colour is scattered the most.
(d) red colour is scattered the most.
Solution: a) light is least scattered.
Q) A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the
blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his textbook. Which of
the following statements is correct?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(d) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
Solution: a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
Q) Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of
light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the same speed as that of the red and the violet light
Solution: c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
Q) The persistence of vision for human eye is
a) 1/10th of a second
b) 1/16th of a second
c) 1/6th of the second.
d) 1/18th of a second
Solution: b) 1/16th of a second
Q) A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect
can be corrected by using lens of power-
(a) +0.5D
(b) -0.5D
(c) +0.2D
(d) -0.2D
Solution: b) -0.5D
Q) The image formed retina of human eye is
a) Virtual and erect
b) Real and inverted
c) Virtual and inverted
d) Real and erect
Solution: b) Real and inverted
Q) The light sensitive cells of retina which are
sensitive to the intensity of light area
a)Cones
b) Rods
c) Both rods and cones
d) None of these
Solution: c) Both rods and cones
Q) The change in the focal length of human eye is caused due to
a) Ciliary muscles
b) Pupil
c) Cornea
d) Iris
Solution: a) Ciliary muscles
Q) The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is
a) 25 m
b) 20 m
c) 25 cm
d) 20 cm
Solution: c) 25 cm
Q) In the following questions a statement of Assertion is followed by a
statement are given-one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason.
(R). Selected the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c)
and (d) as given below:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
i. Assertion (A): Some persons have the difficulty to see the objects in dim
light during night.
Reason (R): Cones respond less to the illumination.
ii. Assertion (A): The colour of the clear sky appears blue.
Reason (R): The sky of the moon appears dark.
iii. Assertion (A): The human eye has more field of view,
Reason (R): For a normal eye, the farthest point up to which the eye can see
objects clearly is infinity.
Solution: i) (c) A is true, but R is false.
ii) (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not correct explanation of the assertion.
iii) (a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
Q) A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass
slab for different values of the angle of incidence (i). He then measures the
corresponding values of the angle of incidence. On analysing these
measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
Solution: (B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
Q) Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the
reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal reflection of light
(d) Reflection of light from the earth
Solution: (b) Scattering of light
Q) Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
Solution: (c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
Q) The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Solution: (b) Reflection of sky in water
Human eye and colourful world important questions: Very Short Answer Questions:
Q) What is Tyndall effect?
Solution: The phenomenon of scattering of a beam of light by colloidal particles, when passed through a colloidal solution, is called the Tyndall effect.
Q) Which of the two is scattered more easily light of shorter wavelength or light of longer wavelength ?
Solution: Light of shorter wavelengths.
Q) Which light has longer wavelength-red light or blue light?
Solution: Red light has longer wavelengths compared to blue light.
Q) As light rays pass from air into a glass prism, are they refracted towards or away from the normal?
Solution: When a light ray passes from air into a glass prism, it bends towards the normal. This happens because of the phenomenon of Refraction of light.
Q) What is the near and far point of a normal eye?
Solution: The near point is about 25 cm and the far point of the eye is at infinity.
Q) What do you understand by dispersion of light?
Solution: The dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours when passed through a transparent medium such as a prism.
Q) State two effects produced by the scattering of light by the atmosphere.
Solution: Two effects produced by the scattering of light by the atmosphere are:
•The Sky appears blue during daytime.
•The Sun appears red at sunrise and sunset.
Human eye and colourful world important questions: Short Answer Questions:
Q) Why do stars seem higher than they actually are? Illustrate your answer with the help of a diagram.
Solution: Due to atmospheric refraction, the stars seem to be higher in the sky than they actually are. This can be explained as follows : Light from a star is refracted (bent) as it leaves space (a vacuum) and enters the earth’s
atmosphere. Air higher up in the sky is rarer but that nearer the earth’s surface is denser.
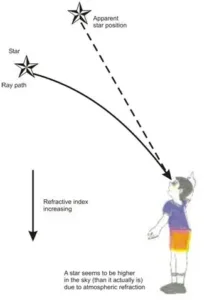
Q) Why do stars twinkle at night?
Solution: Stars twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of starlight.
As the stars are very far away, they behave as almost a point source of light.
When the light coming from stars enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets
refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density.
The path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the
apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering
the eye flickers.
Q) With the help of scattering of light, explain the reason for the difference in colours of the as it appears during sunset/sunrise and noon. (CBSE 2015)
Solution: When there is sunrise or sunset the sun is near the horizon, so the light rays have to cover large distance and hence the blue colour scatters away and far from earth but the red colour scatters near the earth and lesser than blue colour because red has maximum wavelength. At noon the sun is at least possible distance from earth, so the blue colour scatters very less due to that distance and hence we see sun as white in colour, and as blue has minimum wavelength, so the rest of the colours would also not get scattered.
Q) Describe the formation of rainbow in the sky with the help of a diagram.
Solution: When sunlight splits due to water drops suspended in air, causing the band of seven colours is called rainbow. Water droplets acts as tiny prism in the sky. The sunlight when enters these tiny droplets undergo internal reflection and also refract these rays which are dispersed causing a band of seven colours called rainbow. Rainbow is always formed in the direction opposite to the sun.
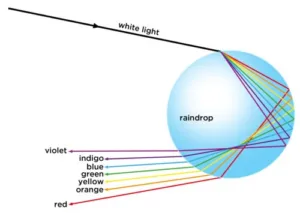
Human eye and colourful world important questions. Pic credit: Pinterest
Q) Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due to gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles. What types of lenses are required by the person suffering from this defect to see the objects clearly.
Solution: Ciliary muscles adjust the focal length of the eye lens. This property is known as power of accomodation.
Presbyopia arisis due to gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles and
diminishing flexibility of eye lens as increasing age of human.
A common type of bi-focal lens consists of both concave and convex parts
required to see objects clearly.
Q) Why the sun appear red while sunset and sunrise ? Explain.
Solution: Red light scatters the least by the molecules present in the air. So at sunrise and sunset, the sunlight travels a longer path through the atmosphere to reach our eyes. The blue light scatters the most and has been mostly removed, leaving the red light remaining which reaches our eyes, hence it appears red.
Q) What is “dispersion of white light”? Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate the recombination of the spectrum of white light. Why it is essential that the two prisms used for the purpose should be identical and placed in an inverted position with respect to each other?
Solution: The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours on passing through a prism is known as the dispersion of white light. This splitting of the light rays occurs because different colours of light bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray, as they pass through a prism.

Human eye and colourful world important questions. Pic credit: Pinterest
It is essential that the two prisms used for the purpose should be identical and placed in an inverted position with respect each other so that the second
prism completely nullifies the dispersion caused by the first prism and we get pure white light.
Q) What is atmospheric refraction? What causes atmospheric
refraction?
Solution: Atmospheric refraction is defined as the refraction of light caused by the earth’s atmosphere. Atmospheric Refraction occurs because the different layers of earth’s atmosphere vary in terms of optical densities.
Q) How are we able to see nearby and also the distant objects clearly?
Solution: The human eye has the ability to accommodate. The eye muscles relax and the lens thins when we need to perceive distant objects. As a result, the focal length of the lens grows, allowing the eye to see farther away objects.
When we need to view anything close by, the eye muscles tighten and the
lens thickens. As a result, the focus length of the lens shortens, allowing the
eye to perceive nearby things.
Human eye and colourful world important questions: Long Answer Questions:
Q) A person needs a lens of power –4.5 D for correction of her vision.
(a) What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
(b) What is the focal length of the corrective lens?
(c) What is the nature of the corrective lens?
Solution: .(a) She is suffering from Myopia (nearsightedness), as the power of the
lens is negative.
(b) The focal length of the corrective lens is:
f = 1 / P
= 1 / -4.5 D
= -0.22 m or -22 cm (negative sign indicates a concave lens)
(c) The corrective lens is Concave in nature, as it is diverging and spreads out
the light rays.
Q) (a) Write the function of each of the following
(i) Cornea
(ii) Iris
(iii) Crystalline
(iv) Ciliary muscles
(b) Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this
phenomenon be observed by an astronaut on the Moon? Give reason to justify
your answer.
Solution: a)i Cornea: If refracts most of the light into eyes.
ii Iris: Gives colour to eyes controls size of pupil.
iii Crystalline Lens: Focuses the image of the object on the retina.
iv Ciliary Muscles: Holds the eye lens and adjusts its focal length.
b)The reason for this occurrence is that the upper layers of the Earth’s
atmosphere are rarer compared to the lower layers. The astronaut who is on the Moon cannot see the Sun reddish during sunrise because the sunlight going towards the Moon does not undergo refraction as there is no atmosphere on the Moon.
Q) (a) A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the black board
placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it.
(b) Why do stars twinkle? Explain.
Solution: a)The defect is Myopia or short-sightedness i.e. Inability of an eye in viewing long distance objects. This defect is caused by an elongation of eye-ball and excessive curvature of the lens. The short-sightedness is corrected by using a concave lens which diverges and shifts the image to the retina.
b)The stars twinkle in the night sky because of the effects of our atmosphere.
When starlight enters our atmosphere it is affected by winds in the atmosphere and by areas with different temperatures and densities. This causes the light from the star to twinkle when seen from the ground.
Q) (a) A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the object
placed beyond 5 m. List two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision
may have arisen. With the help of ray diagrams explain.
(i) Why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 cm
from his eyes.
(ii) The type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this
defect is correct by the use of this lens.
(b) If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is
5 m, find the power of the lens as per the new Cartesian sign convention.
Solution: (a) Two possible reason due to which the defect of vision may have arisen are:
(1) increase in curvature of the lens.
(2) increase in length of the eyeball.
(i) A myopic eye has its far point nearer than infinity. It forms the image of a
distant object in front of its retina. In the given case, student’s far point is 5 m. So, image of the object placed beyond 5 m from his eyes is formed in front of the retina and hence appears blurred. That is why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.
(ii) Since a concave lens has an ability to diverge incoming rays, it is used to
correct this defect of vision. The image is allowed to form at the retina by
using a concave lens of suitable power.
b)Power (P) = 1 / Focal Length (f)
Focal Length (f) = 5 m
P = 1/f
= 1/5
= 0.2 D
Since the focal length is positive, the power is negative (since it’s a concave
lens):
P = -0.2 D
Therefore, the power of the lens is -0.2 diopters.
Thank You For visiting our website. In
Here is the (Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions) PDF download link. Practice the (Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions) PDF download. (Human eye and colourful world important questions/Human eye and colourful world pyqs/Human eye and colourful world most important pyqs with solutions.
⇓
Human eye and colourful world important questions
our website, you get more such educational content so don’t forget to allow the notification for more such content.
For more visit: https://deepblogs.net/category/educational-courses/
For short notes of this chapter, visit:
Human eye and colourful world class 10 notes. Positively read, no questions will come out of this.
For One shot video of this chapter, visit: