Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download:
Acid: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
The word ‘acid’ is derived from the Latin word acidus, akin to acer, which means sour.
Bases: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
Bases are substances that are bitter in taste. Bases have a soapy texture, i.e. they are slippery to touch.
Test to distinguish between Acids and Bases: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
Some chemical substances show a sharp change in their color or odour in an acidic or basic medium.
Such substances are called acid-base indicators. They are:
i. Some indicators show a change in colour
ii. Some indicators show a change in odour.
Indicators that show a change in color: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
Litmus:
- Litmus is a purple coloured dye obtained from lichens that belong to the Thallophyta division of plant kingdom.
- Blue Litmus turns red when the solution is acidic.
- Red Litmus turns blue when the solution is basic.
Turmeric Paste:
- It is yellow in color.
- It remains yellow when acid is added to it.
- It chages its color to red in base.
Hydrangea flowers:
- It is blue in color generally and remains blue when added to acid.
- But turns pink in base.
Phenolphthalein:
- It is a colourless solution and remains colourless in acid.
- But becomes pink in base.
Methyl Orange:
- It is generally orange in colour.
- But it turns red when acid is addded to it.
- And turns yellow when base is added to it.
Indicators that show a change in odour: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
-
- Onion: The paste or juice of an onion loses its smell when added to a base, but it doesn’t change its smell when added to an acid.
- Vanilla: Vanilla’s smell vanishes when added to a base, but it doesn’t vanish when added to an acid.
- Clove oil: Clove oil’s characteristic smell cannot be detected when added to a base.
Classification of Acids Based on Source: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
On the basis of source acids are classified into:
1. Organic
Source: Plants and Animals
- Special Condition:
- C and H are present.
- Atleast one C is bonded directly to H
-
- Lactic acid.
- Acetic acid.
- Formic acid.
- Citric acid.
- Oxalic acid.
- Uric acid.
- Malic acid.
- Tartaric acid.
2. Inorganic:
- Source: Rocks and Minerals (Earth Crust)
- Examples:
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4)
Nitric Acid (HNO3))
Carbonic Acid (H2CO3)
Physical Properties of Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
1. Physical State:
- Acids can be found in various states (solid, liquid, or gas) at room temperature, depending on the specific acid in question.
- For example:
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a liquid at room temperature.
Citric acid (found in citrus fruits) is a solid at room temperature.
Hydrogen chloride (HCl), when dissolved in water, forms
hydrochloric acid, but as a pure substance, it is a gas at room
temperature.
2. Corrosive Nature:
- Many acids are corrosive, meaning they can wear away metals,
skin, and other materials. This property is more pronounced in
strong acids.
3. Electrical Conductivity:
- Acids can conduct electricity when it is added in water.
Chemical Properties of Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
1. Reaction with Metals:
- Acids react with certain metals (like magnesium, zinc, and iron) to produce hydrogen gas (with effervescence )and a corresponding salt.
- The general reaction is: Metal + Acid ⇒ Salt + Hydrogen
2. Reaction with Metals Carbonates/Bicarbonates:
- Acids react with carbonates (CO₃²⁻) and bicarbonates (HCO₃⁻) to produce carbon dioxide gas (CO₂), water (H₂O), and a salt.
- The general reaction is: Acid + Metal Carbonate/Bicarbonate ⇒ Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
3. Reaction with Metal Oxides:
- When acids react with metal oxides, they produce a salt and water.
- This type of reaction is an example of a neutralization reaction, where the basic properties of the metal oxide neutralize the acidic properties of the acid. Thus metallic oxides are basic.
- The general reaction is: Acid + Metal Oxide ⇒ Salt + Water.
Role of Water in Dissociation of Acid : (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
When an acid dissolves in water, it splits into two parts: hydrogen ions (H⁺) and negative ions (like Cl⁻ from hydrochloric acid, HCl). The equation for this dissociation looks like this:
HCl ⇒ H⁺ + Cl⁻
Water helps acids dissociate by pulling apart the acid molecules into ions and stabilizing these ions in solution. This dissociation process is essential for acids to exhibit their characteristic properties, such as acidity.
Arrhenius Acid: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- An ArrheniDureamsing Ouatloucd Sainds is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
- In aqueous solutions, these hydrogen ions usually exist as hydronium ions (H30+), which are formed when hydrogen ions attach to water molecules.
- Example: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions and chloride ions.
Dilute Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- A diluted acid has a relatively small amount of acid (solute) dissolved in a large amount of water (solvent).
- Properties:
⇒Lower concentration of H⁺ ions.
⇒Less corrosive and less reactive.
⇒Lower acidity (less intense).
Concentrated Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- A concentrated acid has a relatively large amount of acid (solute) dissolved in a small amount of water (solvent).
- Properties:
⇒Higher concentration of H⁺ ions.
⇒Very much corrosive and reactive.
⇒Higher acidity (more intense).
Physical Properties of base: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Bases taste bitter – There are very few food materials that are alkaline. It is even more important that care be taken in tasting bases. Tasting bases is more dangerous than tasting acids because of the property of stronger bases to denature protein. Bases feel slippery or soapy.
- Electrical Conductivity: They can conduct electricity. Some bases are great conductors of electricity.
- Corrosive nature: Bases can be highly corrosive to the skin and eyes, bases can be corrosive, especially strong bases.
Chemical Properties of base: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
1) Reaction with metals:
- Bases reacts with amphoteric metals such as Aluminium, Zinc, Lead, Be and tin to form a salt and hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is as follows: Metals + Bases + Water ⇒ Salt + Hydrogen.
2) Reaction with non-metal oxides:
- Bases react with non-metal to form salt and water.
- This is also a type of neutralisation reaction. So it proves that non- metallic oxides are acidic.
- Non- metallic oxides can be acidic or neutral in nature.
- The reaction goes this way: Bases + Non metallic oxides ⇒ Salt + Water.
Strong Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- A strong acid is an acid which is completely ionized in an aqueous solution.
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl) ionizes completely into hydrogen ions and chloride ions in water.
Weak Acids: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- A weak acid is an acid that ionizes only slightly in an aqueous solution.
- Acetic acid (found in vinegar) is a very common weak acid.
pH: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Danish scientist Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen developed the pH scale in 1909 and revised it in 1924.
- pH is a numeric scale that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance or solution.
- The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates acidity, while a pH greater than 7 indicates a base.
- pH paper or universal indicator paper can be used to determine the pH of a solution. The color that develops on the paper is compared to a standard pH color chart.
Usage of pH in daily life: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- pH is important in many areas, including biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, and medicine.
-
pH and soil-Different plants prefer different pH ranges for growth. Soil pH can be affected by acid rain, fertilizers, and other factors.
-
pH and toothpaste-Toothpastes contain basic ingredients that help neutralize the effect of acids and increase the pH in the mouth.
Common Salt: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical Name- Sodium Chloride
- Chemical Formula- NaCl
- Produced by – Neutralisation reaction between an acid and a base
- Source- Sea and Ocean , Rock salt, salty inland lakes.
- Usage-
- Cooking: Salt is added to food for flavor.
- Salt is a primary preservative for pickled vegetables and is used to enhance the flavor of meat products.
- Salt is the most common chemical used for fish fermentation.
- Salt is a raw material for making many chemicals, including sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and baking soda.
Sodium hydroxide: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical formula – NaOH
- Common Name – Caustic soda
- Manufactured by – Chlor-Alkali process
Chlor-Alkali Process: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- The chlor-alkali process is an industrial method for producing chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) by passing an electric current through salt water (brine).
- Products- Chlorine, Hydrogen and NaOH.
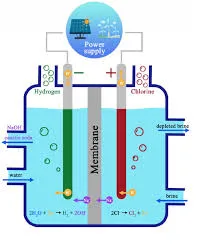
2NaCl + 2H2O ⇒ 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
Calcium oxychloride: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical formula – CaOCl₂
- Common Name – Bleaching powder
- Manufactured by – Hasenclever plant and Beckmann‘s plant
- Principle of manufacture – The chlorine gas obtained as a byproduct from the chlor-alkali process when reacts with dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)₂] produces bleaching powder.
- Uses of bleaching powder- (a) It is used in the textile industry for bleaching
cotton and linen.
(b) it is used as an oxidising agent in chemical
industries.
(c) It is used for disinfecting drinking water by
killing germs.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate/sodium bicarbonate: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical formula – NaHCO₃
- Common Name – Baking soda
- Manufactured by – Ammonia soda process/Solvay‘s process
- Uses of baking soda- (a) It is used to make baking powder (a mixture of baking soda,
mild edible acid such as tartaric acid and cornstarch).
(b) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
(c) It is used as an ingredient of antacid medicines.
Washing Soda: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical formula – Na2CO₃.10H2O
- Common Name – Washing soda
- Manufactured by – Adding water of crystallisation with soda ash (Na2CO3)
- Uses-
- Washing soda can be used as a stain remover, oven cleaner, water spot remover, and laundry booster. It can also be used to unclog drains, remove greasy build-up from pots and pans, and clean outdoor furniture.
- Washing soda can soften hard water.
- Washing soda is used in the manufacture of detergents, soap, paper, glass, and borax.
Plaster of Paris: (Acid bases and salts class 10 short notes pdf download.)
- Chemical formula – CaSO4.1/2H20
- Manufactured by- heating Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O)
- Uses-
- Used to make casts for broken bones and sprains to immobilize the affected area and help it heal
- Used as a protective coating on walls and ceilings, to fill gaps in walls and roofs, and to smooth walls before painting
- Used to make molds and casts for statues, busts, and other decorative elements
Thank You For visiting our website. In our website, you get more such educational content so don’t forget to allow the notification for more such content.
For more visit: https://deepblogs.net/category/educational-courses/