Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Don’t miss at all.
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download:
- Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download: Introduction:
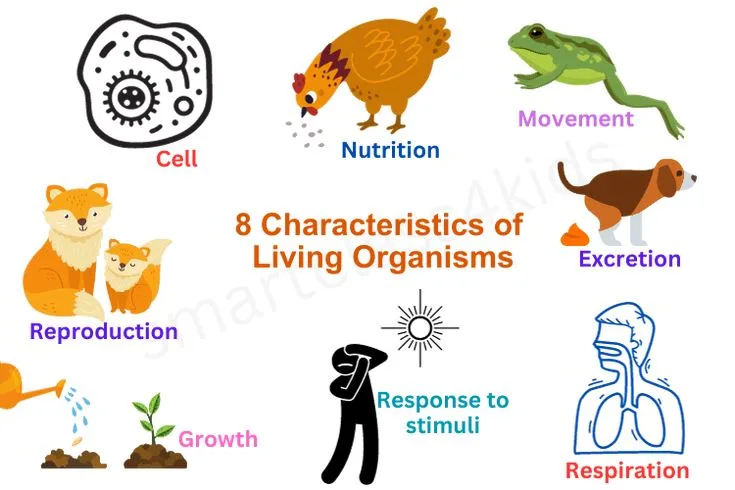
- Characters of Living Organisms:
- What are life Processes:
- Nutrition:
- Types of Nutrition:
- Types of Autotrophic Nutrition:
- Photosynthesis:
- Storage of Glucose:
- Stomata:
- Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition:
- How amoeba obtain its food:
- Paramecium:
- Human Digestive System:
- Mouth:
- Oesophagus:
- Stomach:
- Liver:
- Pancreas:
- Small Intestine:
- Large Intestine:
- Breathing:
- Respiration:
- Exchange of gases in plants:
- Human Respiratory System:
- Alveoli:
- Haemoglobin:
- Diaphragm:
- Inhalation vs Exhalation:
- How do fishes breathe:
- How do insects breathe:
- Transportation:
- Functions of Blood:
- Composition of blood:
- Heart:
- Why there are chambers in heart:
- Lymphatic System:
- Lymph:
- Functions of Lymphatic System:
- Transportation in Plants:
- Ascent of Sap:
- Xylem:
- Root Pressure:
- Phloem:
- Excretion:
- Kidney:
- Nephron:
- Formation of Urine:
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download:
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download: Introduction:
Characters of Living Organisms:
- Nutrition
- Respiration
- Movement
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Excretion
- Sensitivity
What are life Processes:
- The basic and essential activities performed by a living organism to sustain and maintain life.
- There are four basic life processes:
1.Nutrition
2.Respiration
3.Transportation
4.Excretion
Nutrition:
- The process of deriving and utilization of food is called nutrition.
- Food gives us:
⇒Energy
⇒Growth & development
⇒Repairing of tissues
Types of Nutrition:

Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
- Autotrophic nutrition-Organisms that prepare their own food.
E.g., Green plants, Algae, Cyanobacteria, etc. - Heterotrophic nutrition- Organisms that are dependent on other organisms
for food.
E.g., Animals, fungi, etc.
Types of Autotrophic Nutrition:
- Photosynthetic -Autotrophic nutrition- A type of autotrophic nutrition in which organisms
prepares their own food by utilizing light energy.
E.g.:Green plants,Cyanobacteria,Algae, Euglena - Chemosynthetic – Autotrophic nutrition- A type of autotrophic nutrition in which organisms
prepares their own food by utilizing chemical energy.
E.g., Purple sulfur bacteria
Photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis occurs in green plants containing chlorophyll
- Chlorophyll is the green pigment which absorbs light) present in chloroplasts.
- Chloroplasts is present in the leaf cells ( mesophyll cells of leaf)
- steps of photosynthesis: (i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and
splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Storage of Glucose:
- Plants store glucose in the form of “starch”
- Humans store glucose in the form of “glycogen”
Stomata:
- Stomata are tiny pores like structure present on surface of leaves.
- Functions of stomata:
1. Transpiration
2. Exchange of gases during photosynthesis and respiration. - The opening and closing of the pore is controlled by kidney bean shaped cells called guard cells.
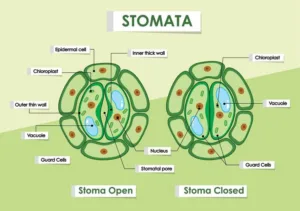
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition:
- Holozoic nutrition-
Organisms feed by ingesting whole food material. Food is digested and absorbed inside the animal body. Examples: Cow, goat, deer,Lion, tiger,Human being, Amoeba,Paramecium - Parasitic nutrition-
Organisms derive nutrition from plants or animals without killing them. They obtain nutrition by living on or inside the host. Examples: Tapeworm,Lice,Ticks,Leech,Ascaris,Cuscuta (plant) - Saprophytic nutrition-
Organisms feed on dead and decaying matter. Food is digested externally and then nutrients are absorbed. Examples-Bread mold, Mushroom,Yeast
How amoeba obtain its food:
- Amoeba obtains food through a process called phagocytosis, or endocytosis:
- Amoeba extends temporary arm-like extensions called pseudopods from its cell surface
- The pseudopods encircle and engulf food particles or live prey
- The pseudopods fuse over the food particles to form a vacuole
- Once the food is trapped, the amoeba secretes digestive enzymes to break down the food into simpler molecules
- The simpler molecules then diffuse into the amoeba’s cytoplasm
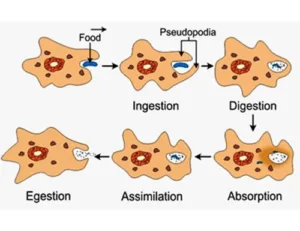
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Paramecium:
- It is an unicellular, eukaryotic organism. They are characterized by the presence of thousands of cilia covering their body. They are found in freshwater, marine and brackish water.
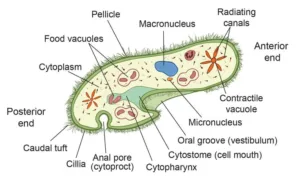
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Human Digestive System:
- Alimentary canal: A long hollow tube which contains organs through which the food actually passes (Oesophagus,stomach, small intestine, large intestine, etc.)
- Accessory organs: Organs that helps in digestion but no food passes through them (liver, pancreas, salivary glands, etc.)
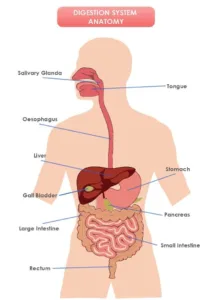
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Mouth:
- Food is ingested.
- Crushed and chewed with the help of teeth.
- Food is wetted with saliva to make its passage smooth.
- Food is mixed with saliva with the help of muscular tongue.
Oesophagus:
- Food is pushed downwards due to rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles and is known as peristaltic movements.
Stomach:
- Stomach is a large J-shaped organ which expand when food enters.
- The muscular walls of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
- Gastric Juices- 1) Pepsin: Enzyme that breaks down proteins. Works only in acidic medium.
2)HCl: Makes the medium acidic
3)Mucus: Protects inner lining of the stomach from HCl.
- Increased secretion of HCl cause acidity.
Liver:
- Secretes Bile juice.
- Bile juice is stored in gall bladder
- Bile juice makes food alkaline.
- Bile juice helps in emulsification of fats.
Pancreas:
- Secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes like:
1)Trypsin – helps in digestion of proteins.
2)Lipase – helps in breakdown of emulsified fats.
3)Pancreatic amylase – helps in digestion of carbohydrates.
Small Intestine:
- 5-7 meters long
- Site of final ingestion
- Secretes intestinal juice
- Food in small intestine is absorbed by these finger like structure called villi.
- Villi are finger-like projections which increases the surface area for absorption.
- Richly supplied with blood vessels which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body.
- Food is utilized for obtaining energy, building up new tissues and the repair of old tissues.
Large Intestine:
- All the unabsorbed food is sent into the large intestine.
- Absorption of water takes place in large intestine.
- Removal of undigested and unabsorbed food is done by anus.
Breathing:
- It is exchange of gases (Oxygen and carbon dioxide)
- It has 2 steps:
1.Inhalation: Taking air inside the body.
2.Exhalation: Releasing air outside the body.
Respiration:
- Respiration refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH)
- Types of respiration- 1) Aerobic and 2) Anaerobic
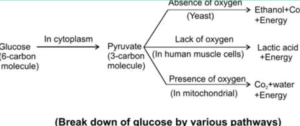
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download.
Exchange of gases in plants:
- Done with the help of stomata.
- Lower surface of leaf has more stomata, upper part of leaf has less stomata.
- At night, when there is no photosynthesis occurring, CO2 elimination is the major exchange activity going on. During the day, CO2 generated during respiration is used up for photosynthesis, hence there is no CO2 release. Instead, oxygen release is the major at this time.
Human Respiratory System:
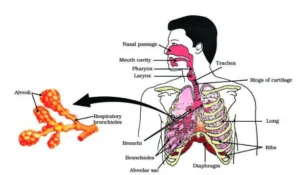
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
- Rings of cartilage are present in the throat. These ensure that the air passage does not collapse.
- In human beings air is taken into the body through the nostrils.
- The air passing through the nostrils is filtered by fine hair that line the passage. The passage is also lined with mucus which helps in this process.
Alveoli:
- Balloon-like or sac like structure.
- Wall of alveoli are only one celled thick and provide a surface where the exchange of gases can taken place.
- Contain an extensive network of blood vessels which helps in exchange of gases.
- The blood brings carbon dioxide from the rest of the body for release into the alveoli, and the oxygen in the alveolar air is taken up by blood in the vessels to be transported to all the cells in the body.
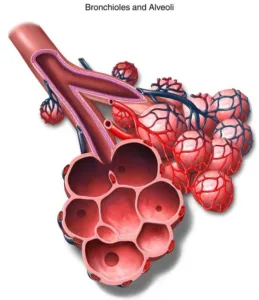
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Haemoglobin:
- Respiratory pigment
- Iron containing protein
- Provides red color to RBC
- Affinity of Hemoglobin for various gases: CO > O2 > CO2
Diaphragm:
- It is a thin skeletal muscle that sits at the base of the chest and separates the abdomen from the chest.
Inhalation vs Exhalation:

Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download.
How do fishes breathe:
- Gills are the respiratory organs for fishes. Fishes take in oxygen which is dissolved in water through gills.
- Since, availability of oxygen is less in the aquatic environment, so the breathing rate of aquatic organisms is faster.
How do insects breathe:
- Insects have a system of spiracles and tracheae which is used for taking in oxygen.
Transportation:
- Transportation is a life process which allows useful substances such as oxygen, food, salts, carbondioxide, nitrogenous wastes and other substances in a multicellular organism to move from one part of the body to another.
- Transportation is done by-
- 1. Blood- Red colored fluid connecting tissues. Transport and protective function.
- 2. Blood vessels (Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries)- Blood vessels are the network of tubes through which blood is pumped around the body
- 3. Heart- The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to cells and tissues, and removing waste products
Functions of Blood:
1)Transport function:
- Digested food substances
- Excretory products (from tissue to excretory organs)
- Hormones
- Heat
- O2 (from lungs to rest of the body)
2)Protective function:
- Guards against infection
- Blood clotting
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Composition of blood:
- Plasma- Liquid content or fluid part of the blood. Pale yellowish in colour
- RBCs- Bi Concave shape. On maturity – Nuclear absent. Red due to “Hemoglobin”. Function- Transports O2
- WBCs- Nucleus is present. Provides Immunity. Function- Produce antibodies against Pathogens
- Platelets- Function- Responsible for blood clot formation.
Heart:
- Muscular organ
- Located in chest cavity tilted towards left lung
- As big as fist
- It is a blood pumping organ
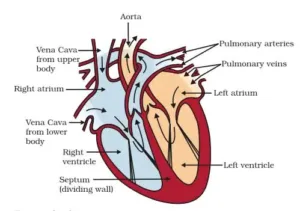
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
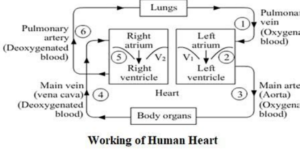
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download.
Why there are chambers in heart:
- To prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- More oxygen will be supplied to body organs in better way.
- Highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- More respiration leading to more energy production.
Note- Mammals have double circulation.
Lymphatic System:
1.Lymph fluid
2.Lymph vessels
3.Lymph nodes
Lymph:
- Lymph is a colorless fluid formed due to leakage of plasma from blood capillaries. RBCs are absent in lymph while WBCs are present.
Functions of Lymphatic System:
- Lymph facilitates absorption of fats and fat-soluble nutrients back to the circulatory system.
- It removes excess fluid from body tissue and maintains balance of fluid between blood and tissues.
- It forms part of the body’s immune system and helps defend against bacteria and other microbes, by producing immune cells like lymphocytes and other antibody cells.
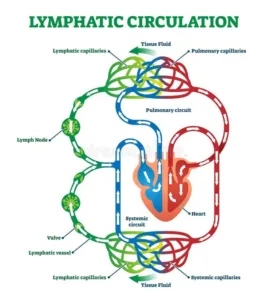
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Transportation in Plants:
- Transportation is a life process which allows useful substances such as oxygen, food, salts, carbondioxide, wastes and other substances in a multicellular organism to move from part of the body to another.
- Materials- 1.Oxygen
2.Carbon dioxide
3.Water
4.Food (glucose, sucrose)
5.Minerals (Nitrogen, Phosphorus)
6.Hormones
7.Waste substances - If the distance between two cells is small, diffusion and osmosis occurs.
- If the distance become large between two cells because of changes in plant body. Diffusion and osmosis will not be sufficient. A proper system of transportation is therefore essential in such situations.
Ascent of Sap:
- The upward movement of water and minerals from the root to the upper part of the plant against the gravity via xylem tissue is called ascent of sap.
Xylem:
- Xylem is made up of four types of elements:
Vessels (main water conducting tubes or
channels)
1.
Tracheids (main water conducting tubes and
channels)
2.
3.Xylem fibres (provide structural support)
4.Xylem parenchyma (storage of food material)
Root Pressure:
- When water enters into root cells by the process of osmosis a pressure is generated in the roots which helps in transporting the water and other ions from the soil in upward directions into the xylem. This hydrostatic pressure is known as root pressure.
Phloem:
- Phloem is made up of four types of elements:
1.Sieve tubes (food transport)
2.Companion cells (food transport)
3.Phloem parenchyma (storage)
4.Phloem fibres (support)
Excretion:
- The biological process involved in the removal of harmful
metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion. - Metabolic wastes: Carbon dioxide
Excess water
Excess mineral salts
Nitrogenous waste
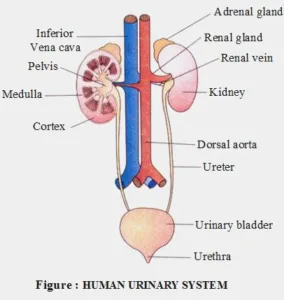
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Kidney:
- The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body that are responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and controlling the body’s fluid balance.
- Blood and waste enter through real entry.
- Filtered blood leaves through renal vein.
- Excess water and toxic waste leaves through ureter as urine.
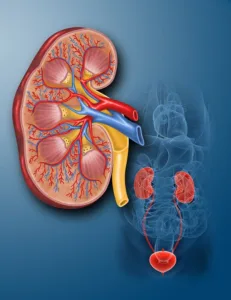
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Nephron:
- Structural & functional unit of kidney/excretion system
- Responsible for filtration of blood.
- There are millions of nephron in each kidney.
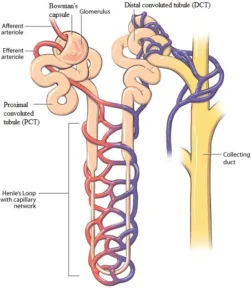
Biology class 10 chapter 1 life process notes pdf free download. Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 life processes short Notes PDF free Download. Pic Credit: Pinterest
Formation of Urine:
1 . Glomerular filtration:
Nitrogenous wastes, glucose, water, amino acid, excessive salts from the blood are filtered and initial filtrate enters into Bowman capsule of the nephron.
2. Selective reabsorption:
Useful substances like glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water from the filtrate are reabsorbed back by capillaries surrounding the nephron.
3. Tubular secretion:
Urea, extra water and salts are secreted into the tubule which open up into the collecting duct & then into the ureter.
Thank You.
For more notes and question answers, visit: https://deepblogs.net/category/educational-courses/
Normally I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very forced me to try and do so Your writing style has been amazed me Thanks quite great post