Internal Vs External injury, find out which one has more impact on your body
An injury is defined as physical harm or damage to someone’s body caused by an accident or an attack. It can also refer to harm or damage done to a living thing. In a broader sense, injury may also encompass harm or damage to a business or its reputation.
Here are some key points about injuries(Internal Vs External injury):
- Physical Injury: A physical injury refers to any harm or damage inflicted on the body. It can be classified into two main types: external injuries(Internal Vs External injury), which affect the skin or outer body surfaces (such as cuts, bruises, and burns), and internal injuries(Internal Vs External injury), which impact internal organs or structures (like internal bleeding, organ damage, and fractures).
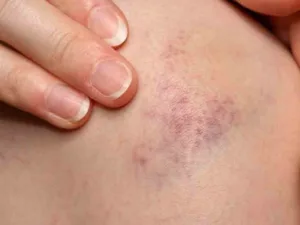
image credit pinterest
- Physical injuries(Internal Vs External injury) can result from various causes, including accidents, falls, sports activities, or violence, and they require appropriate medical assessment and treatment to ensure proper healing and recovery.
- Psychological Injury: A psychological injury(Internal Vs External injury) refers to harm to a person’s mental and emotional well-being. It can result from traumatic events such as abuse, accidents, natural disasters, or prolonged stress, and may lead to conditions like anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or other mental health issues(Internal Vs External injury).
- Unlike physical injuries, psychological injuries(Internal Vs External injury) may not have visible symptoms but can significantly impact a person’s behavior, thoughts, and overall quality of life. Treatment often involves therapy, counseling, and sometimes medication to support recovery and emotional healing.
- Legal Injury: A legal injury(Internal Vs External injury) refers to harm or damage that affects an individual’s legal rights or interests. This type of injury can arise from violations of laws, contracts, or civil rights, and can include financial losses, property damage, defamation, or breaches of duty. Legal injuries (Internal Vs External injury) often result in disputes that are addressed through the legal system, where the injured party(Internal Vs External injury) may seek compensation or other remedies through lawsuits or legal claims.
Injuries can occur in various contexts, from sports and workplace accidents to car crashes and criminal acts. The severity of an injury can range from minor to life-threatening.
Internal and external injuries(Internal Vs External injury) are two broad categories of injuries that differ based on their location and the cause of the injury.
Here’s a brief outline of the main differences of External and Internal injuries:
- External Injuries(Internal Vs External injury):
- These are injuries that occur to the outside of the body.
- They are often caused by an outside force or trauma(Internal Vs External injury), such as cuts, abrasions, lacerations, or burns.
- External injuries are usually visible to the eye and can include penetrating wounds (like stab wounds) or non-penetrating wounds (like bruises or concussions).
- Internal Injuries(Internal Vs External injury):
- These injuries(Internal Vs External injury) happen inside the body and may not be immediately visible.
- They can be caused by blunt trauma or an impact that forces the body to absorb energy, leading to damage of internal organs or internal bleeding.
- Internal injuries can also result from medical conditions or diseases that impair circulation, nervous system functions, or lead to a decreased supply of blood, oxygen, or nutrients to certain areas of the body(Internal Vs External injury) .
Understanding External Injuries:
Types of External Injuries:
(i) Cuts and Lacerations:
Cuts and lacerations are terms used to describe injuries that result in a break in the skin, though they have slightly different meanings:
- Cuts: These are injuries where the skin has been split or separated due to contact with a sharp object. Common causes include accidents with knives, tools, or broken glass.
- Lacerations: These imply a more jagged or irregular tear in the skin, often caused by blunt trauma that crushes or stretches the skin beyond its capacity to remain intact.
Both cuts and lacerations can vary in depth and severity, potentially affecting not just the skin but also underlying tissues like muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels(Internal Vs External injury). They can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the hands, arms, legs, head, and face due to their exposure and interaction with the environment.
(ii) Bruises (Contusions):
Bruises, also known as contusions, are a type of external injury that occurs when small blood vessels under the skin(Internal Vs External injury) are damaged due to an impact or pressure, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissues. Here’s a brief description:
- Appearance: Bruises typically present as discoloration on the skin, starting as a reddish mark that turns blue or purple, and eventually yellow or green as it heals.
- Causes: They are commonly caused by bumps, falls, or blunt force that compresses the skin against the underlying structures.
- Common Locations: Bruises can appear anywhere on the body but are frequently seen on areas that are prone to injury(Internal Vs External injury), such as the arms, legs, and torso.
image credit pinterest
While bruises are generally minor and heal on their own, severe bruising, especially around vital organs, can be more serious and require medical attention. If a bruise is unusually large, painful, or accompanied by swelling, it’s advisable to seek professional medical advice.
(iii) Burns:
Burns are a type of external injury(Internal Vs External injury) that occurs when skin or other tissues are damaged by heat, electricity, radiation, or chemicals. Here’s a brief overview:
- Thermal Burns: These are caused by external heat (Internal Vs External injury) sources such as flames, hot liquids (scalds), hot solids, or steam.
- Chemical Burns: Result from contact with substances like strong acids, alkalis, or certain petroleum products, which can cause skin and deeper tissue necrosis.
image credit pinterest
- Electrical Burns: Occur due to the passage of electric current through the body(Internal Vs External injury) , potentially causing extensive deep tissue damage.
- Radiation Burns: Caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn) or other radiation sources.
Burns are classified by their depth:
- Superficial Burns: Affect only the outer layer of the skin(Internal Vs External injury), causing redness and pain.
- Partial-Thickness Burns: Extend into some of the underlying skin layer, leading to blisters and severe pain.
- Full-Thickness Burns: Go through the full depth of the skin, destroying both layers and possibly affecting underlying tissues.
The severity of burns is also assessed by the percentage of total body surface area (TBSA) involved. Burns can lead to complications like hypovolemic shock, infection, scarring, and contractures. Treatment may include fluid resuscitation, topical antibacterials, cleansing, elevation, skin grafting, and intensive rehabilitation.
It’s crucial to treat burns correctly to prevent further damage and promote healing. For minor burns, keeping the area clean and applying an antibiotic salve may suffice. However, more serious burns require professional medical treatment to manage pain, prevent infection, and address any complications. Always seek immediate medical attention for severe burns.
(iv) Abrasions:
Abrasions, commonly known as scrapes, are a type of external injury where the top layer of skin is worn away due to friction or scraping against a rough surface. Here’s a brief description:
- Types of Abrasions:
- Linear or Scratch Abrasions: Caused by a minor injury, like a nail scratch, that strips away the epidermis.
- Patterned Abrasions: Occur when an object presses into the skin, leaving an impression. These can be pressure abrasions from extended compression (like a tight sock) or impact abrasions from a forceful blow.
- Grazed or Brush Abrasions: Result from friction against a broad surface, such as falling onto pavement and skinning a knee. These can vary in depth and are sometimes called brush burns if prolonged.
- Symptoms:
- Quick bleeding that clots soon
- Swelling and redness
- Pain or tenderness
- Possible bruising around the area
- Common Causes:
- Physical trauma like falls or blows
- Impact against uneven or hard surfaces
- Extended pressure from objects
- Common Locations:
- Frequently reported on the head, torso, legs, knees, arms, and elbows due to their exposure and likelihood of contact with surfaces during activities.
(v) Fractures:
Fractures are a type of external injury that occurs when there is a break or crack in a bone. They can range from minor cracks to complete breaks and can affect any bone in the body. Here’s a brief overview of fractures related to external injuries:
- Types of Fractures:
- Simple Fracture: The bone is broken but there is no open wound in the skin.
- Compound Fracture: The broken bone pierces the skin, creating an open wound and increasing the risk of infection.
- Comminuted Fracture: The bone shatters into several pieces.
- Greenstick Fracture: The bone cracks on one side only, not all the way through.
- Hairline Fracture: A partial fracture of the bone, often difficult to detect with standard X-rays.
- Pathological Fracture: Occurs when an underlying disease weakens the bone, leading to a fracture with minimal trauma.
- Common Causes:
- Trauma: Such as falls, accidents, or sports injuries.
- Overuse: Repetitive motion can lead to stress fractures, especially in athletes.
- Osteoporosis: Weakens bones, making them more susceptible to breaks from minor stresses.
- Symptoms:
- Pain: Often severe and immediate.
- Swelling: Around the affected area.
- Deformity: The limb or affected area may look out of place.
- Inability to Move: The injured area without significant pain.
- Bruising: Discoloration around the injured area.
- Treatment:
- Immobilization: Using casts, splints, or braces to keep the bone in place during healing.
- Medication: For pain relief.
- Surgery: In some cases, to align the bones and secure them with pins, plates, or screws.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to restore movement and strength after the bone has healed.
Symptoms and Diagnosis For External Injuries:
When it comes to external injuries, healthcare professionals look for several key symptoms and use various methods for diagnosis:
- Visual Indicators:
- Bleeding: The presence of blood, which may range from minor to severe.
- Swelling: An increase in size of the injured area, often indicating inflammation or accumulation of fluids.
- Redness: Often accompanies swelling and indicates inflammation.
- Pain and Discomfort:
- Immediate Pain: Can be sharp and intense, indicating the severity of the injury.
- Delayed Pain Response: Sometimes pain or soreness develops hours after the injury, which can be indicative of certain types of soft tissue damage.
- Medical Assessment:
- Visual Examination: The first step in assessing an injury, looking for cuts, abrasions, bruising, or deformities.
- Palpation: Gently pressing on the injured area to assess pain response and the extent of injury.
- Range of Motion Tests: To determine if movement is restricted or causes pain.
- X-rays: Commonly used to visualize bone fractures or dislocations.
- MRI or Ultrasound: May be used for a more detailed view of soft tissue injuries like ligament tears or muscle strains.
It’s important to note that while some symptoms can be assessed visually or through self-reporting of pain, others require professional medical equipment and expertise to diagnose accurately. If you suspect a serious injury, it’s always best to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment and First Aid For external injuries:
Treatment and first aid for external injuries are crucial to prevent complications and promote healing. Here’s a general guide:
- Assess the Situation: Ensure the scene is safe before providing aid. If the injury is severe, call for emergency medical services immediately.
- Stop the Bleeding:
- Apply direct pressure on the wound with a clean cloth or gauze.
- If blood soaks through, add more layers without removing the initial dressing.
- Elevate the injured limb above the heart level, if possible, to slow bleeding.
- Clean the Wound:
- Gently clean with soap and warm water.
- Rinse out soap to avoid irritation.
- Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or iodine, which can damage tissue.
- Protect the Wound:
- Apply an antibiotic cream to reduce the risk of infection.
- Cover with a sterile bandage.
- Change the bandage daily to keep the wound clean and dry.
- Give Care for Specific Injuries:
- For bruises, apply a cold pack to the area for no more than 20 minutes to reduce swelling and pain.
- For burns, cool the burn under running water for at least 20 minutes, then cover with a clean, dry cloth or dressing.
- Monitor for Shock:
- Look for signs like pale or clammy skin, rapid breathing, or weakness.
- Have the person lie down with their feet elevated, if possible.
- Seek Professional Medical Care:
- If the wound is deep, has jagged edges, or there’s concern about foreign material inside.
- If there are signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, or pus.
- If the person hasn’t had a tetanus shot in the past five years for puncture wounds or deep cuts.
Remember, this is a general and primary guide for External injuries. Always you all should follow the most current first aid practices and seek professional medical advice when in doubt. Stay calm, act quickly, and ensure the injured person receives the care they need and go to hospital quickly.
Understanding Internal Injuries:
Types of Internal Injuries:
(i) Organ Damage:
Organ damage is a specific type of internal injury where the structure or function of an internal organ is impaired. This can result from either trauma or disease. In the context of trauma, organ damage can be caused by:
- Blunt Trauma: Occurs when a body part collides with something else, usually at high speed, causing blood vessels inside the body to tear or crush.
- Penetrating Trauma: Happens when a foreign object pierces the body, tearing a hole in one or more blood vessels.
The most serious sources of internal bleeding due to trauma, which can lead to organ damage, include:
- Head Trauma: With internal bleeding (intracranial hemorrhage).
- Bleeding Around the Lungs: Known as hemothorax.
- Bleeding Around the Heart: Referred to as hemopericardium and cardiac tamponade.
- Tears in Large Blood Vessels: Near the center of the body, such as the aorta and its major branches.
Symptoms of organ damage due to internal injuries can vary depending on the type of trauma and the organ involved. Common symptoms may include:
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: From internal bleeding in organs like the liver or spleen.
- Light-headedness, Dizziness, or Fainting: Due to significant blood loss.
- Deeply Purple Skin: Called ecchymosis, resulting from bleeding into the skin and soft tissues.
- Pain and Swelling in the Leg: Often caused by a fracture of the thighbone.
- Headache, Seizures, or Loss of Consciousness: Could indicate internal bleeding in the brain.
Organ damage can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. If you suspect someone has internal injuries, especially with symptoms like those mentioned, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical services right away.
(ii) Internal bleeding:
Internal bleeding is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood leaks from the circulatory system into areas inside the body. It can result from trauma, such as an accident or injury, or from non-traumatic causes like a ruptured aneurysm or a bleeding disorder. Here’s a brief overview of internal bleeding related to internal injuries:
- Symptoms:
- General: Dizziness, weakness, fainting, low blood pressure, acute visual problems, numbness, or severe headache.
- Head: Difficulty with speech, vision, swallowing, or coordination; changes in alertness or consciousness.
- Chest or Abdomen: Abdominal pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, blood in urine, or black, tarry stools.
- Muscles or Joints: Pain, swelling, decreased range of motion.
- Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: To check for signs of internal bleeding.
- Imaging Tests: Such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds to locate the source of bleeding.
- Laboratory Tests: To assess blood count and clotting function.
- Treatment:
- Emergency Care: For severe cases, including blood transfusions and surgery to stop the bleeding.
- Medications: To address underlying conditions like blood clotting disorders.
- Monitoring: In hospital settings, especially if the bleeding is related to trauma.
- Complications:
- Shock: Due to significant blood loss.
- Organ Failure: If the bleeding isn’t controlled promptly.
- Death: In severe cases where treatment is not received in time.
Internal bleeding can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. If you suspect someone has internal injuries with symptoms like those mentioned, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical services right away.
(iii) Traumatic Brain Injuries for internal injuries:
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a serious condition that occurs when an external force injures the brain. TBIs can range from mild concussions to severe brain damage and are a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Here’s a detailed look at TBIs:
- Symptoms:
- Physical: Headaches, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, problems with speech, loss of balance, and fatigue.
- Sensory: Blurred vision, ringing in the ears, changes in the ability to smell, and sensitivity to light or sound.
- Cognitive: Memory or concentration problems, mood swings, depression, anxiety, and changes in sleep patterns.
- Causes:
- Falls, vehicle-related collisions, sports injuries, violence, and combat injuries are common causes of TBIs.
- Diagnosis:
- TBIs are diagnosed using the Glasgow Coma Scale to assess consciousness, along with imaging tests like MRI and CT scans to detect brain pathology.
image credit pinterest
- Treatment:
- Treatment may include medication to manage symptoms, surgery to repair damage, and rehabilitation to regain function.
- Prevention:
- Wearing helmets, using seat belts, and creating safe environments can help prevent TBIs.
TBIs require immediate medical attention. If you suspect someone has a TBI, especially if they show symptoms like confusion, loss of consciousness, or severe headache, seek emergency medical services right away. For more detailed information, you can refer to the resources provided by reputable health organizations.
Soft tissue injuries for internal injuries
Soft tissue injuries refer to damage to the tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body, excluding bones. These injuries typically involve the muscles, tendons, and ligaments and can occur due to various reasons, including physical trauma and overuse. Here’s a brief overview:
- Types of Soft Tissue Injuries:
- Sprains: Injuries to ligaments, the tough bands connecting bones in a joint.
- Strains: Injuries to muscles or tendons, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscles to bones.
- Contusions: Also known as bruises, these occur when small blood vessels are damaged or broken as the result of a blow to the skin.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation or irritation of a tendon.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, which are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints.
- Symptoms:
- Pain: Varies depending on the injury but is often the first symptom.
- Swelling: Due to inflammation or bleeding within the tissue.
- Bruising: Caused by blood pooling under the skin.
- Limited Range of Motion: Due to pain or swelling.
- Weakness: In the affected area, making it difficult to use the injured part of the body.
- Causes:
- Acute Trauma: Such as a fall, twist, or blow to the body.
- Overuse: Repeated motions can cause micro-tears in the tissue over time.
- Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: To assess pain, swelling, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: Like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to view the extent of the injury.
- Functional Tests: To evaluate the stability of the affected area.
- Treatment:
- R.I.C.E. Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation to reduce pain and swelling.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical Therapy: To restore strength and flexibility.
- Surgery: In severe cases, to repair torn tissue.
It’s important to treat soft tissue injuries properly to prevent further damage and ensure a good recovery. If you suspect a soft tissue injury, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Symptoms and Diagnosis For internal injuries:
Symptoms and diagnosis of internal injuries are critical for providing timely and effective treatment. Here’s an overview:
- Symptoms of Internal Injuries:
- General Symptoms: Dizziness, severe weakness, passing out, low blood pressure, acute visual problems, numbness, weakness on one side of the body, severe headache.
- Head: Difficulty with speech, vision, swallowing, or chewing; changes in alertness, including sleepiness, lethargy, or stupor; loss of consciousness.
- Chest or Abdomen: Abdominal pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, blood in urine, black, tarry stool.
- Muscles or Joints: Pain, swelling, decreased range of motion in a joint.
- Shock: Rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, especially if a substantial amount of blood is lost.
- Diagnosis of Internal Injuries:
- Physical Examination: To check for signs of internal bleeding and assess the overall condition.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds to locate the source of bleeding and assess the extent of the injury.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood count and clotting function tests to evaluate the body’s ability to stop bleeding.
Internal injuries can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. If you suspect someone has internal injuries, especially with symptoms like those mentioned, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical services right away. For more detailed information, you can refer to resources provided by reputable health organizations.
Treatment and First Aid
Treating internal injuries requires prompt medical attention, as they can be life-threatening. Here’s a general guide on the treatment and first aid for internal injuries:
- Call for Emergency Help: If you suspect internal injuries, call emergency services immediately.
- Monitor ABCs:
- Airway: Ensure the airway is clear.
- Breathing: Check if the person is breathing.
- Circulation: Look for signs of circulation such as movement, coughing, or breathing.
- Control External Bleeding: If there’s also external bleeding, apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage.
- Keep the Person Still: Avoid moving the person unless necessary, as movement could worsen internal bleeding or damage.
- Positioning: If there are no injuries to the spine, pelvis, or hips, and the person is breathing, lay them down and elevate their legs to increase circulation to the heart.
- Treat for Shock: Keep the person warm and comfortable. Loosen tight clothing and cover them with a blanket.
- Do Not Give Anything to Eat or Drink: Especially if the person is going into surgery, as this could cause complications.
- Provide Comfort and Reassurance: Stay with the person and reassure them help is on the way.
Preventing external injuries is crucial for safety and well-being. Here are some prevention and safety tips:
- Protective Gear:
- Helmets: Wear properly fitted helmets to protect against head injuries while biking, skating, or playing contact sports.
- Pads: Use knee and elbow pads in sports that involve a risk of falling or collision.
- Appropriate Clothing: Wear clothing suitable for the activity, including footwear that provides good support and traction.
- Safe Practices:
- Proper Techniques: Learn and apply the correct techniques for sports and physical activities to reduce the risk of injury.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Engage in warm-up exercises before activities and cool-down exercises afterward to prepare your muscles and reduce the risk of strains and sprains.
- Environment Safety:
- Home and Work: Keep living and working spaces free of hazards such as loose rugs, wet floors, and clutter that can cause trips and falls.
- Playgrounds: Ensure that children’s play areas are equipped with shock-absorbing materials, such as mulch or sand, to cushion falls.
- Education:
- First Aid Training: Learn basic first aid to respond effectively to common injuries.
- Safety Rules: Educate yourself and others about the safety rules and regulations relevant to your activities.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Equipment: Regularly inspect and maintain sports equipment and playgrounds to ensure they are in good condition and safe to use.
- Awareness:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on new safety recommendations and practices for your activities.
- Supervision: Ensure that children are supervised when engaging in potentially hazardous activities.
Preventing Internal Injuries:
1. Seatbelts and Airbags: In Vehicles
- Seatbelts: Always wear a seatbelt while driving or riding in a vehicle. Seatbelts help to keep you securely in place, reducing the risk of severe internal injuries in the event of a crash.
- Airbags: Ensure your vehicle is equipped with functioning airbags. Airbags provide a cushion that helps protect your head, neck, and torso from impact during collisions.
2. Fall Prevention: In Homes and Workplaces
- Home Safety: Install handrails on staircases, use non-slip mats in bathrooms, and keep walkways clear of obstacles. Proper lighting is essential to prevent trips and falls.
- Workplace Safety: Use appropriate safety gear, such as harnesses when working at heights. Ensure that floors are dry and free of hazards, and use ladders and step stools properly.
3. Awareness of Body Mechanics: During Physical Activities
- Proper Techniques: Learn and use correct techniques for lifting, carrying, and other physical tasks to avoid straining muscles and injuring internal organs.
- Warm-Up and Stretching: Engage in proper warm-up and stretching exercises before physical activities to prepare your body and reduce the risk of internal injuries.
- Ergonomics: Arrange your workspace to support good posture and reduce strain on your body, particularly when sitting for long periods or performing repetitive tasks.
Here are some real-life examples and case studies that illustrate external and internal injuries:
External Injuries
- Sports Injuries: A football player suffers a compound fracture in his leg during a tackle. The bone pierces through the skin, requiring immediate medical attention, surgery, and a lengthy rehabilitation process.
- Kitchen Accidents: A chef sustains deep cuts and lacerations on her hand while chopping vegetables due to a slip of the knife. Proper wound care and stitches are necessary to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Workplace Incidents: A construction worker experiences abrasions and contusions after falling from scaffolding. The impact causes superficial damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue bruising.
Internal Injuries
- Car Accidents: A driver involved in a high-speed collision suffers from internal bleeding and organ damage, specifically a ruptured spleen, which is diagnosed via CT scan and requires emergency surgery.
- Sports Impacts: A hockey player receives a heavy blow to the head, leading to a traumatic brain injury (TBI). Symptoms include confusion and loss of consciousness, necessitating immediate medical evaluation and treatment.
- Falls from Heights: An individual falls from a ladder, resulting in a pulmonary contusion—bruising of the lung tissue. This is characterized by chest pain and difficulty breathing and is confirmed through imaging tests.
These examples highlight the diverse nature of injuries that can occur in various settings and the importance of appropriate response and treatment to ensure the best possible outcomes for those affected. Remember, prevention through safety measures and protective gear is key to reducing the risk of such injuries.
FAQs:
Q1: What are internal injuries? A1: Internal injuries refer to harm that occurs inside the body, affecting organs, blood vessels, or other internal structures. Common examples include internal bleeding, organ damage, and closed fractures.
Q2: What are external injuries? A2: External injuries are visible damages to the body’s outer surface, such as cuts, bruises, burns, and abrasions. These injuries typically affect the skin or underlying tissues and are often easier to diagnose and treat.
Q3: How can I tell if someone has an internal injury? A3: Signs of internal injuries can include severe pain, swelling, dizziness, fainting, difficulty breathing, and visible bruising without an apparent external cause. Internal injuries often require medical imaging for accurate diagnosis.
Q4: What should I do if I suspect an internal injury? A4: If you suspect an internal injury, seek immediate medical attention. Avoid moving the person unnecessarily and keep them as still and comfortable as possible until help arrives.
Q5: How are external injuries treated? A5: Treatment for external injuries includes cleaning and dressing wounds, applying ice to reduce swelling, using bandages or sutures for cuts, and administering pain relief. Severe external injuries may require more advanced medical care.
Q6: Can an external injury lead to internal injuries? A6: Yes, a severe external injury, such as a deep cut or a major impact, can cause internal damage. For example, a significant blow to the abdomen can result in both external bruising and internal organ damage.
Q7: How are internal injuries diagnosed? A7: Internal injuries are typically diagnosed using medical imaging techniques like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasounds. Blood tests and physical examinations are also used to assess the extent of the injury.
It’s important to treat these injuries properly to prevent infection and ensure proper healing. For minor injuries, cleaning the wound and applying a bandage may be sufficient, while more severe injuries might require medical attention, such as stitches or surgery. Always seek professional medical advice if you’re unsure about the severity of an injury.
You all can share your experience about any kind of internal or external injuries that you had faced? And How did you handle it?, Share your experience in comment section.
More visit: https://taazakhobor.in/
More you can read:
https://deepblogs.net/difference-between-allopathyhomeopathy-and-ayurveda/
The Impact of AI in Human Careers Opportunities: Will AI destroy Human’s career in 21st century?
How to Recover Your Business From Bankruptcy in 2024!!
Diabetes: A Global Epidemic in the 21st century
Practical Education vs Theoretical Education