Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: What is Light?:
- Light is a form of energy which gives sensation of vision.
- Light itself is not visible otherwise Universe would not be black.
- Light is a Non-mechanical transverse wave, that is why it travels in vacuum.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: What is Optics?:
- Optics is study of light.
- There are two branches of optics:
Ray optics: Particle nature of light
Wave optics: Wave nature of light
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Ray nature of light:
- Light also has the property of a particle. The intensity of the light varies depending on the number of particles. Bright light has many particles while dark light has fewer particles. These particles of light are called “photons”.
- Light travels at a speed of about 300,000 kilometers per second (c = 3 x 10^8 m/s).
- When in a vacuum such as outer space where no matter is present, light travels straightforward, this is called Rectilinear motion of light.
- Several photons in a single line constitute a light ray.
- Several light rays constitute a beam of light.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Laws of reflection:
- The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like mirrors, smooth metal surface, and clear water.
- The Laws of reflection states that
1)The incident ray, the reflected ray and Normal all lie in the same plane.
2)The Angle of incidence (< i) = The angle of reflection ( <r)
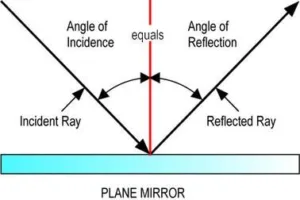
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained. Pic credit: Pinterest
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Spherical Mirrors:
1) Concave Mirrors:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained. Pic credit: Pinterest
2) Convex Mirrors:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained. Pic credit: Pinterest
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Some Important terms:
- Principal axis – A line joining the center of curvature and pole is called principal axis.
- Principal Focus – A point on the principal axis of a spherical mirror where the rays of light parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to meet after reflection is called principal focus it is denoted by F.
- Focal length – The distance between the pole and principal focus of a spherical mirror is called focal length.
- Optical center – It is a point on the principal axis of the lens such that a ray passing through goes undeviated.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Rules to obtain image:
1. A ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus after reflection.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained.
2. A ray passing through the principal focus will become parallel to principal axis after reflection.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained.
3. A ray passing through center of curvature will follow the same path back after reflection.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained.
4. Ray incident at pole is reflected back making same angle with principal axis.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Uses of Concave Mirrors:
- Shaving mirrors.
- Vehicle headlights.
- Searchlights.
- Makeup mirrors.
- Microscopes.
- Telescopes.
- Solar cookers.
- Flashlights.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Uses of Convex Mirrors:
- When convex mirrors are used, the magnification of objects becomes simple.
- It is used in sunglasses.
- It is used as a rear-view mirror in automobiles.
- It’s utilised in ATMs and other places for security reasons.
- It’s used as a reflector for street lights.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Image Formation In Concave Mirrors:
1.Object at Infinity:
- Size of image – Highly diminished,
point sized. - Nature of image – Real and
inverted
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained
2. Object beyond C
- Size of image – Diminished
- Nature of image – Real and
inverted
3. Object at C
- Size of image – Same size
- Nature of image – Real and
inverted
4. Object between C & F
- Size of image – Enlarged
- Nature of image – Real and
inverted
5. Object at F
- Size of image – Highly enlarged
- Nature of image – Real and
inverted
6. Object between F and P
- Size of image – Enlarged
- Nature of image – Virtual and
erect
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Image Formation In Convex Mirrors:
1. Object at infinity
- Size of image – Highly diminished,
point sized. - Nature of image – Virtual and
erect
2. Object at finite distance
- Size of image – Diminished
- Nature of image – Virtual and
erect
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Sign Convention In Mirrors:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Important Formulas:
1) Mirror formulae: 1/f= 1/v + 1/u
2) Magnification formula: m= height of image(h’)/height of object(h) = -v/u
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Refraction of Light:
- Refraction of light is the change in the direction of a light ray passing from one medium to another.
- The bending of light ray is caused due to the differences in optical density between the two transparent media.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Laws of Refraction of Light:
- The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. This is also knowns as Snell’s law of refraction.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Rules of Refraction of Light:
1.Rarer to denser (Bends towards normal)
2.Denser to rarer (Bends away from normal)
Note: Refraction doesnot occur when light is incident normally or n light transits through media having same optical density.
Refraction through glass slab:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Refractive Index:
- The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media.
- Absolute refractive index: If medium 1 is vacuum or air, the the refractive index of medium m is considered with respect to vacuum. This is called the absolute refractive index of the medium.
- Relative refractive index: The refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is given by the ratio of the speed of light in medium 1 and the speed of light in medium 2.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Spherical Lenses:
1) Convex Lens:
2) Concave lens:
Note:
- A lens has two principal foci. They are represented by F1 and F2.
- The distance of the principal focus from the optical center of a lens is
called its focal length.
- Thin Lenses: Lenses with an aperture much smaller than their radius
of curvature.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Rules to obtain image through lens:
i. A ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a convex lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the lens.
In case of a concave lens, the ray appears to diverge from the principal focus located on the same side of the lens.
ii. A ray of light passing through a principal focus, after refraction from a convex lens, will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
A ray of light appearing to meet at the principal focus of a concave lens, after refraction, will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
iii. A ray of light passing through the optical centre of a lens will emerge without any deviation.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Image Formation by Convex Lens:
1. Object at infinity:
2. Object beyond 2F1
3. Object at 2F1
4. Object between 2F1 and F1
5. Object at F1
6. Object between F1 and O
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Images Formation by Concave Lens:
1. Object at infinity
2. Object at a finite distance
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Uses of Convex and Concave lens:
- It is used as Hypermetropia i.e., to correct far-sightedness.
- It is used in microscopes, telescopes and magnifying glasses to subject all the light to a specific object.
- It is used in camera lenses because they focus light for a clear picture.
- In Daily Life. The uses of concave lenses in daily life are in the form of shaving glasses.
- In Ophthalmology.
- In Camera.
- In Flashlight.
- In Medical Equipment/ Lasers.
- In Binoculars.
- In Peepholes.
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Sign Convention of lens:
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Important Formulas:
1) Lens Formula: 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
2) Magnification: m= h’/h = v/u
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Power of the lens:
- It is the degree of convergence or divergence of incident light on a concave or convex surface.
- SI unit – Dioptre or meter^(-1)
- P = 1/f
Light reflection and refraction class 10 physics complete and short notes fully explained: Combination of lenses:
- If n lenses are in contact:
- If n lenses are in contact then,
Power = P1 + P2 + P3 + ………..+ Pn
For more such educational content, visit: https://deepblogs.net/category/educational-courses/