PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download. Most important questions.
- PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: MCQ:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: One Word Question Answer:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: Assertion and Reason type of Question:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
- PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download Link:
PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download:
We are providing you the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download for 2024-25 preparation of your board exam. Theses are the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download. These PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download will help you to preapare better for your exam.
So try these PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download. These PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download are provided in this website and the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download link is given at the extreme bottom for later use.
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download link. These are the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download, you can practise them from here. For later use, download the pdf from the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution link given below.
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: MCQ:
Q) Focal length of plane mirror is:
a) At infinity
b) Zero
c) Negative
d) None of these
Solution: a) At infinity
Q) A concave mirror gives real, inverted and same size image if the object is placed:
a) At F
b) At infinity
c) At C
d) Beyond C
Solution: c) At C
Q) Power of the lens is -40D , its focal length is:
a) 4m
b) -40m
c) -0.025m
d) 25m
Solution: c) -0.025m
Q) Image formed by plane mirror is:
a) Real and erect
b) Real and inverted
c) Virtual and erect
d) Virtual and inverted
Solution: c) Virtual and erect
Q) A concave mirror gives virtual, erect and enlarged image of the object.
The position of the object is:
a) At infinity
b) Between F and C
c) Between P and F
d) At F
Solution: c) Between P and F
Q) The radius of curvature of a mirror is 20cm, the focal length is:
a) 20cm
b) 10cm
c) 40cm
d) 5cm
Solution: b) 10cm
Q) In optics an object which has higher refractive index is called:
a) Optically rarer
b) Optically denser
c) Refractive index
d) Optical dense
Solution: b) Optically denser
Q) Convex lens focuses a real, point-sized image at the focus. The object is placed:
a) At focus
b) Between F and 2F
c) At infinity
d) At 2F
Solution: c) At infinity
Q) The optical phenomena, twinkling of stars, is due to:
a) Atmospheric reflection
b) Total reflection
c) Atmospheric refraction
d) Total refraction
Solution: c) Atmospheric refraction
Q) The unit of power of lens is:
a) Metre
b) Centimeter
c) Diopter
d) M-1
Solution: c) Diopter
Q) A student obtains a blurred image of distant object on a screen using a convex
lens. To obtain a distinct image on the screen he should move the lens.
(A) away from the screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) to a position very far away from the screen.
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the
object.
Solution: (B) towards the screen
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: One Word Question Answer:
Q) Fill in the blanks:
(i) Image formed by a plane mirror is always________and__________
(ii) A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, faces
towards the centre of the sphere, is called a_____________
(iii) The focal length of a spherical mirror is equal to _______ its radius of
curvature.
(iv) Speed of light is_________
(v) Light rays always travels in______________
Solution: (i) Virtual and erect
(ii) Concave mirror
(iii) Half of
(iv)3 × 10⁸ m/s
(v) Straight lines
Q) Answer in one word/one sentence.
(i) A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an
object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
(ii) The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
(iii) An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal
length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
(iv) Define the principal focus of a concave mirror
Solution: .(i) Given:
Object distance, u = -10 cm (negative because it’s in front of the mirror)
Magnification, M =-v/u = 3 (since the image is three times magnified)
From the magnification formula, M=-v/u , we can rearrange it to solve for
v = u × M
Substituting the values, we get :v= 3 × (-10) = -30 cm
The negative sign indicates that the image is formed in the same side as the
object, meaning it’s a real image. Thus, the image is located 30 cm in front of
the mirror and it’s inverted
(ii)The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1 which means that size of
the image formed is exactly equal to the size of the object and is formed
behind the mirror.
The positive sign shows that the image formed is virtual and erect.
(iii)Given:
Object distance (u) = -10 cm (negative since object is on the left side of the
mirror)
Focal length (f) = 15 cm (positive since it’s a convex mirror)
Using the mirror formula:
1/v = 1/f – 1/u
Substituting the values:
1/v = 1/15 – 1/-10
1/v = 1/15 + 1/10
1/v = 5/30
v = 6 cm
The image distance (v) is 6 cm
The nature of the image:
Since the image distance (v) is positive, the image is virtual and erect..
(iv) The principal focus is the point where parallel rays of light converge or
appear to diverge after reflecting from a concave mirror.
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: Assertion and Reason type of Question:
Q) Assertion (A): The bottom of a tank or pond, filled with water appears to be
raised.
Reason (R): The apparent depth of the tank is given by I /n times the original
depth.
(a) (A) is incorrect and (R) is correct.
(b) (A) is correct and (R) is incorrect.
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Solution: (d) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Q) Assertion (A): The shaving mirrors are convex mirrors.
Reason (R): Convex mirror always forms a virtual image.
(a) (A) is incorrect and (R) is correct.
(b) (A) is correct and (R) is incorrect.
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Solution: (b) (A) is correct and (R) is incorrect.
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q) The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to air are 3/2 and 4/3
respectively. If speed of light in glass is 2x 108 m/s, find the speed of light in water.
(CBSE 2016)
Solution: Given:Refractive index of glass (μg) = 3/2
Refractive index of water (μw) = 4/3
Speed of light in glass (vg) = 2x 10⁸ m/s
We can use the relationship between refractive index and speed of light:
Refractive index (μ) = Speed of light in vacuum (c) / Speed of light in medium(v)
For glass:
μg = c / vg
vg = c / μg = 3x 10⁸ m/s / (3/2) = 2 x 10⁸m/s (given)
For water:
μw = c / vw
vw = c / μw = 3 x 10⁸ m/s / (4/3) = 2.25 x 10^8 m/s
Therefore, the speed of light in water is 2.25 x 10^8 m/s.
Q) “A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of
an object placed in front of it”. Same the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams
to justify the above statement.
Solution: The lens described is a convex (converging) lens.
A convex lens can form both a magnified, erect image and a magnified,
inverted image of an object placed in front of it.
Ray Diagrams: Magnified, Erect Image: Object between F and 2F
results in a magnified, erect, and real image.
Ray diagram shows parallel ray refracting through F, ray through F
refracting parallel to axis, and center ray continuing undeviated
Magnified, Inverted Image: Object beyond 2F results in a magnified,
inverted, and real image.
Ray diagram shows parallel ray refracting through F, ray through F
refracting parallel to axis, and center ray continuing undeviated
Q) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30
cm. List four characteristic (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
(CBSE 2017)
Solution: Object distance (u) = -15 cm (negative because it’s in front of the lens)
Focal length (f) = -30 cm (negative because it’s a concave lens)
Using the lens formula: 1/v = 1/f – 1/u
Substituting the values: 1/v = 1/-30 – 1/-15
1/v = -1/30 + 1/15
1/v = -1/30 + 2/30
1/v = 1/30
v = 30 cm
So, the image distance (v) is 30 cm.
Since the image distance is positive, the image is virtual and appears on the
same side of the lens as the object.
Magnification (M) = -v/u = -30/-15 = 2 (positive, indicating an erect image)
characteristics of the image:
– Nature: Virtual
– Position: On the same side of the lens as the object
– Size: Smaller than the object
– Orientation: Erect
Note: The negative sign in the magnification formula is cancelled out by the
two negative values, resulting in a positive magnification, indicating an erect
image.
Q) What is meant by power of a lens? Write its Sl unit. A student uses a lens of focal
length 40 cm and another of 20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens.
(CBSE 2018)
Solution: The power of a lens is a measure of its ability to converge or diverge light. It
is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length of the lens.
The SI unit of power of a lens is diopter (D).
Now, let’s analyze the given lenses:
Lens with focal length 40 cm:
Focal length (f) = 40 cm = 0.4 m (converted to meters)
Power (P) = 1/f = 1/0.4 = 2.5 D
Since the power is positive, this lens is a convex lens (converging lens).
Lens with focal length 20 cm:
Focal length (f) = 20 cm = 0.2 m (converted to meters)
Power (P) = 1/f = 1/0.2 = 5 D
Since the power is positive, this lens is also a convex lens (converging lens).
– The 40 cm lens is a convex lens with a power of 2.5 D.
– The 20 cm lens is a convex lens with a power of 5 D.
Q) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term ‘absolute refractive index
of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in
vacuum.
(CBSE 2018)
Solution: Laws of Refraction of Light:
•The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal to the interface at the
point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
• The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (i) to the sine of the angle of
refraction (r) is a constant for the given pair of media. This constant is called
the refractive index (n) of the second medium with respect to the first
medium. Mathematically, Snell’s law states:
n = sin(i) / sin(r)
Absolute Refractive Index:
The absolute refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of light in
vacuum (c) to the speed of light in that medium (v):n = c / v
This expression relates the absolute refractive index of a medium to the speed
of light in that medium. The absolute refractive index is a fundamental
property of the medium and is dimensionless.
Q) If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed
in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it?
(CBSE 2018)
Solution: Convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image of the
object placed at any position in front of the mirror
Q) A ray travelling in water enters obliquely into glass. Does the light bend
towards or away from the normal and why?
Solution: When light travels from a medium with a lower refractive index (water) to a
medium with a higher refractive index (glass), the light bends towards the
normal.
This is because the speed of light decreases when it enters the medium with a
higher refractive index (glass). According to Snell’s law, the angle of refraction
is smaller than the angle of incidence, causing the light to bend towards the
normal
Q) A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to principal axis of a convex lens of
focal length 10 em. If the object is placed 30 cm away from the lens, find the
position, size and nature of image.
Solution: Given:
Focal length (f) = 10 cm
Object distance (u) = -30 cm (negative since object is on the left side of the
lens)
Substituting the values in the lens formula:
1/10 = 1/-30 + 1/v
1/v = 1/10 – 1/30
1/v = 2/30
v = 15 cm
The image distance (v) is 15 cm.
The magnification (m) can be calculated using the formula:
m = v/u
m = 15/-30
m = -0.5
The negative sign indicates that the image is inverted.
The size of the image can be calculated as:
Image height = m × Object height
Image height = -0.5 × 5 cm = -2.5 cm
Therefore, the position of the image is 15 cm from the lens, the image is real,
inverted, and 2.5 cm in size.
Q) Light enters from air to kerosene having a refractive index of 1.47. What is the
speed of light in kerosene ?
Solution: Light enters from air to kerosene having a refractive index of 1.47:
The speed of light in kerosene can be calculated using the formula:
v = c/n
Where:
v = speed of light in kerosene
c = speed of light in vacuum (3 x 10^8 m/s)
n = refractive index of kerosene (1.47)
Substituting the values:
v = 3× 10⁸ m/s / 1.47
v = 2.04 × 10⁸ m/s
Therefore, the speed of light in kerosene is 2.04 × 10⁸m/s.
Q) A compound lens is made up of two thin lenses having power + 12.5 D and-2.5
D. Find the focal length and power of the combination.
Solution: A compound lens is made up of two thin lenses having power +12.5 D & -2.5 D:
The focal length (f) of the combination can be calculated using the formula:
1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
Where f1 and f2 are the focal lengths of the individual lenses.
Given:
Power of lens 1 = +12.5 D
Power of lens 2 = -2.5 D
Focal length of lens 1, f1 = 1/12.5 = 0.08 m
Focal length of lens 2, f2 = 1/-2.5 = -0.4 m.
Substituting in the formula:
1/f = 1/0.08 + 1/-0.4
1/f = 12.5 – 2.5
1/f = 10 m Therefore, the focal length of the combination, f = 1/10 = 0.1 m
The power of the combination is the sum of the powers of the individual lenses:
Power = +12.5 D + (-2.5 D) = 10 D
Q) Refractive indices of medium A, B and Care 1.3, 1.5 and 1.4 respectively. In
which of the following the speed of light will be the:
(a) fastest
(b) slowest and why?
Solution: Refractive indices of medium A, B and C are 1.3, 1.5 and 1.4 respectively:
(a) The speed of light will be fastest in medium A.
The speed of light in a medium is inversely proportional to the refractive index of
that medium. Since medium A has the lowest refractive index of 1.3, the speed of
light will be the fastest in this medium.
(b) The speed of light will be slowest in medium B.
Medium B has the highest refractive index of 1.5, so the speed of light will be the
slowest in this medium.
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download: LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS:
Q) (a) What happens to a ray of light when it travels from one medium to another
having equal refractive indices?
(b) State the cause of refraction of light.
Solution: (a)When a ray of light travels from one medium to another having equal
refractive indices, it does not bend or refract. The ray continues in the same
direction, without any change in its path.
(b) The cause of refraction of light is the difference in the refractive indices of
the two media. When light travels from a medium with a higher refractive
index to a medium with a lower refractive index, it bends away from the
normal. Conversely, when light travels from a medium with a lower refractive
index to a medium with a higher refractive index, it bends towards the normal
Q) One half of a convex lens is covered with black paper.
(a) Mention the position and nature of the image.
(b) Will there be any difference in image obtained if the lens is uncovered? Give reasons for your answers.
Solution: (a) When one half of a convex lens is covered with black paper and an object is
placed at 2F:
The image formed will be real, inverted, and diminished.
The position of the image will be between F and 2F on the side of the
uncovered portion of the lens.
The ray diagram will show: A ray parallel to the principal axis refracting
through the focal point (F).
A ray passing through the optical center continuing undeviated.
The intersection of these rays forms the real, inverted, and diminished
image between F and 2F.
(b) Ray Diagram for Uncovered Lens: When the same object is placed at the
same position in front of the same lens but now uncovered:
The image obtained will be the same as in the case of the covered lens.
There will be no difference in the image obtained in the two cases because
the uncovered portion of the lens will still contribute to the formation of
the image.
The nature, position, and size of the image will remain real, inverted, and
diminished, respectively, as the uncovered portion of the lens will still
refract light to form the image.
Q) (a) If the image formed by a mirror for all position of the object placed in
front of it is always diminished, erect and virtual, state the type of the mirror. Write one use such mirrors
are put to and why.
b) Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirror. Find the nature and focal
length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm.
Solution: (a) The type of the mirror is convex mirror.
Use of convex mirror:
Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror in vehicles as it always produce
virtual, erect and diminished image of an object. So, images of vehicles that
are spread over a large area can be seen easily in it.
(b) Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is defined as the distance
between center of curvature and pole of the mirror.
For a spherical mirror, the focal length is related to the radius of curvature (R)
by the formula:
Given, radius of curvature, R = +24 cm.
Substituting the given value of R = +24 cm, we get
f = +24 cm/2 = +12 cm
Therefore, the focal length of the convex mirror with a radius of curvature of
+24 cm is +12 cm.
Q) . (a) Define 1 dioptre of power. Find the focal length of a lens of power-2.0 D.
(b) Why does a lemon kept in water in a glass tumbler appear to be bigger than
actual size?
Solution: .(a)1 diopter is the power of a lens of focal length 1 meter. This means that if
a lens has a focal length of 1 meter, its power is defined as 1 diopter.
The focal length of a lens of power -2.0 D can be calculated using the formula:
1/f = P
where f is the focal length and P is the power of the lens.
Substituting the value of power, we get:
1/f = -2.0 D
f = -0.5 m
Therefore, the focal length of the lens is -0.5 m
(b)The lemon appears to be bigger than its actual size due to the refraction of
light as it passes from the water to the air. The refractive index of water is
higher than that of air, so the light bends towards the normal as it passes from
the water to the air. This causes the lemon to appear larger than its actual size.
Q) A thin converging lens forms a (i) real magnified image, (ii) virtual magnified
image.
(a) Write the position of object in each case,
(b) Draw labelled diagram for each case.
Solution: . (a) (i) For a real magnified image formed by a converging lens, the object
must be placed between the focal length and 2F1.
(ii) For a virtual magnified image formed by a converging lens, the object must
be placed between the focal length and optical lens.
(b) (i)
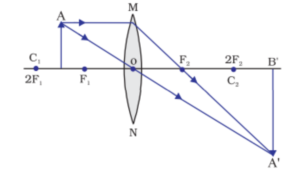
(i) Real Magnified image
(ii)
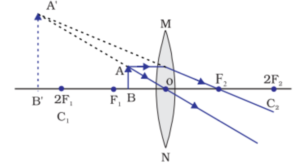
(ii)Virtual Magnified Image
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download Link:
Here is the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution link. Practice the PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution. PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution.
⇓
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download
PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution. PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download with solution. PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download. PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download. PYQS of light reflection and refraction class 10 pdf download/PYQS of light physics class 10 pdf download.
For more such content, visit: https://deepblogs.net/category/educational-courses/
For the notes of this chapter visit:
For one shot video:
